Annual inflation in the euro area and in Greece registered a new slowdown in May, but the threshold set by the European Central Bank is 2%.
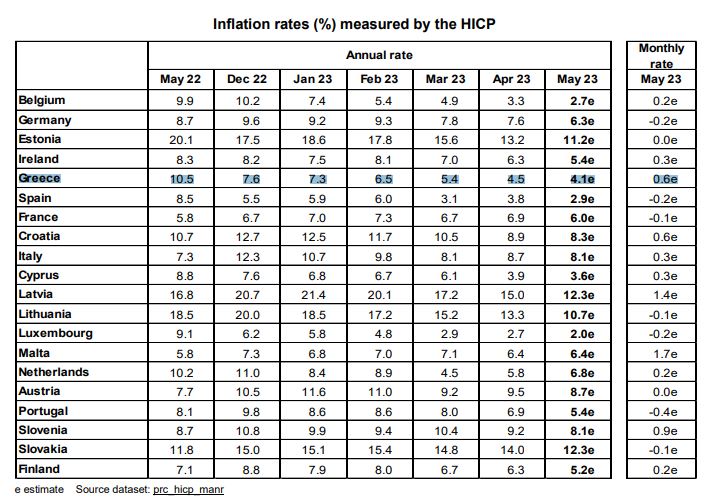
In particular, annual inflation slowed down to 6.1% in May from 7.0% in April, according to the initial estimate of Eurostat. Data from the European Statistical Agency showed a further slowdown in inflation in Greece to 4.1% in May from 4.5% in April and 10.5% a year earlier.
It is worth noting that the analysis of the European Statistical Office showed that the category of food, alcohol and tobacco are expected to show the largest annual gains in May (12.5% from 13.5% in April), followed by non-energy manufactured goods (5.8% from 6.2% in April), services (5.0% from 5.2% in April) and energy (-1.7% from 2.4% in April).
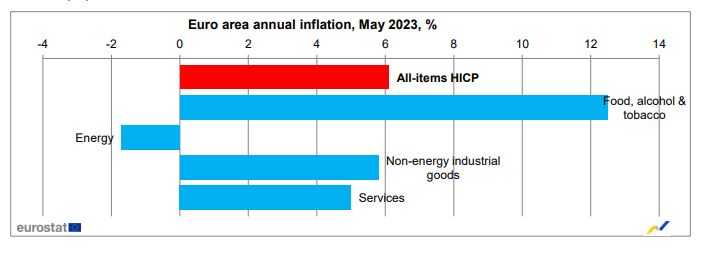
In addition, core inflation, which excludes food and fuel price hikes and played an important role in the ECB’s policy meetings, fell to 5.3% from 5.6%. The result was better than the 5.5% expected by economists.
However, in Greece it seems inflation trend continues. Characteristically, producer prices in the industry showed a significant decline for the second month in a row in April 2023, which is another example downward trend in inflation.
In particular, according to ELSTATthe general producer price index in industry (total domestic and foreign market) with the base year 2015 and the reporting month April 2023 compared to the corresponding index in April 2022 showed a decrease of 13.3% compared to an increase of 48.8%, as noted with a corresponding comparison of the indicators of 2022 with 2021.
However, food prices remain very high.. Characteristically, the growth in food inflation recorded by ELSTAT for April 2023 amounted to 11.4%. This equates to an increase of 11.3% recorded by the Statistics Office a year ago, in April 2022.
However, energy prices in April 2022 showed an increase of 57.6%, and in April of this year they recorded a decrease of 17.8%. The reasons for this different course are that food prices are affected by two factors: the cost of energy and the cost of other inputs, as well as problems in the supply chain that have not yet been overcome. At the same time, many experts believe that in parallel with this, there are problems of unfair competition.





More Stories
The Greek Tax Administration sent out "letters" 20,000 taxpayers who "forgot" declare income
Tax returns 2024: which income is exempt or subject to special tax
Tax returns: platform open for legal entities