The war between Israel and Hamas, now in its 16th day, raises serious fears that the entire Middle East will “ignite.” As the Israeli army prepares for a ground offensive in Gaza, in the north of the country, on the border with Lebanon, it must confront the threat from Hezbollah.
Tel Aviv today warned that Hezbollah was dragging Lebanon into war, with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu threatening the terror group with “unthinkable” retribution. Meanwhile, the United States has made it clear that if the conflict escalates, it will not hesitate to resort to military intervention. Everyone, of course, is afraid not so much of Lebanon or Syria (whose airports were again hit by Israeli strikes today) as of Iran. Iran’s Foreign Minister warned today that if Israel does not stop its military actions, the entire region will spin out of control.
If Iran decides to enter the war, even indirectly by giving orders to the extremist organizations it controls in Lebanon, Syria and Iraq, it will immediately face sanctions (though it has been under them for many years). And in this case, he will almost certainly take retaliatory measures. How? Closure of the Strait of Hormuz.
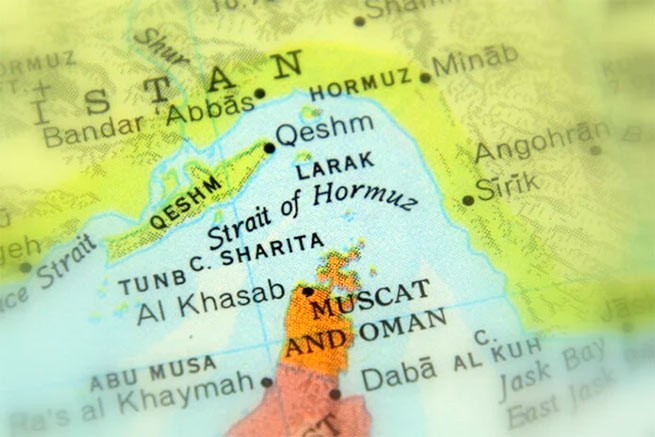
What are the Straits of Hormuz
They are considered the most important oil “artery” on the planet and are located between Oman and Iran, connecting the Persian Gulf in the north with the Gulf of Oman in the south and the Arabian Sea beyond. Their width at their narrowest point is 33 km, and the length of the shipping route is only 3 km in each direction. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are trying to find alternative ways to bypass the straits, including building additional oil pipelines.
Why their closure is a concern
About a fifth of the world’s total oil consumption passes through the straits every day. According to data from the analytical company Vortexa, presented by Reuters, between January and September 2023, an average of 20.5 million barrels per day (b/d) of oil and petroleum products will pass through the Strait of Hormuz.
OPEC members Saudi Arabia, Iran, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait and Iraq export most of their crude oil through the strait. Qatar, the world’s largest exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), sends almost all of its LNG through the straits.
About 80 million metric tons, or 20% of the world’s LNG flow, passes through the straits each year, Vortex said. Oil prices have already overcome the barrier of $92 per barrel, and gas prices – $50 per MWh.
US and Israeli steps
The US Fifth Fleet, based in Bahrain, is tasked with protecting commercial shipping in the region. Iran has threatened to cut off oil supplies through the Strait of Hormuz if the United States actively intervenes in the war or tries to strangle its economy. The Israeli army is preparing for a ground invasion of the Gaza Strip to destroy Hamas, raising the risk of a wider conflict.
Oil embargo scenario
Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amirabdolahian several days ago called on Muslim countries to impose an oil embargo and other sanctions against Israel, but OPEC sources rejected such a scenario.
In 1973, Arab producers, led by Saudi Arabia, imposed an oil embargo against Western countries that supported Israel in the war with Egypt, in particular Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, Great Britain and the United States. If at that time Western countries were the main buyers of oil produced by Arab countries, today the main buyer of oil produced by OPEC is Asia.
Incidents from past years
Reuters has compiled all the explosive past incidents related to the Strait of Hormuz:
- During the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988), both sides tried to cut off oil exports to each other in the so-called “tanker war.”
- In July 1988, the USS Vincennes shot down an Iranian plane, killing all 290 people on board. Washington said it was an accident and Tehran said it was a deliberate attack.
- In early 2008, the United States said Iranian ships were threatening three of its Navy ships in the strait.
- In July 2010, the Japanese tanker M Star was attacked in the strait by the Abdullah Azzam Brigades, an extremist group linked to al-Qaeda.
- In January 2012, Iran threatened to block the strait in response to US and European sanctions aimed at stopping the development of Tehran’s nuclear program.
- In May 2015, Iranian ships hijacked a container ship in the strait and fired on a Singapore-flagged tanker that they said destroyed an Iranian oil platform.
- In July 2018, President Hassan Rouhani hinted that Iran might cut off oil trade in the straits in response to US efforts to stop exports.
- In May 2019, four ships, including two Saudi tankers, were attacked off the coast of the UAE near Fujairah, one of the world’s largest fuel supply centers.
- located near the Strait of Hormuz.
- In January 2021, Iran seized a South Korean-flagged tanker in the waters of the Persian Gulf and arrested its crew.
- In May 2022, Iran arrested 2 Greek ships in response to the arrest of an Iranian ship in Greece at the request of the United States. The ships were released only after 6 months. Greece had to return, at its own expense, the oil confiscated and previously transferred to the Americans.
- In December 2022, the US military said an Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps vessel came within 150m of US warships in the strait.
- In May 2023, Iran seized two oil tankers passing through the straits in retaliation for the US seizure of Iranian tankers.
- In July 2023, the US Navy said it had intervened to prevent Iran from seizing two commercial tankers in the Gulf of Oman. The Navy said in a statement that since 2021, Iran has “harassed, attacked or seized approximately 20 internationally flagged merchant vessels.”






More Stories
Timothy Snyder: "We should think that Russia cannot lose, but…"
Disappointing forecast for the war in Europe
Conflict Intelligence Team: a house in Belgorod was probably destroyed by Russian ammunition