In the conditions of the energy crisis, many are looking for alternative ways to heat the room, using fireplaces, wood and coal stoves, gas appliances. However, if used incorrectly, the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning increases.
What is carbon monoxide
The concentration of carbon monoxide or carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide or carbon monoxide, chemical formula CO) cannot be determined without special equipment. It is formed in combustion conditions with a lack of oxygen, is colorless and odorless, and is extremely toxic to humans. It can accumulate when working indoors:
- charcoal grills;
- fireplaces;
- wood, gas and coal stoves;
- kerosene heaters;
- internal combustion engines of automobiles;
- faulty gas water heater;
- gasoline generators.
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous?
Once in the blood, carbon monoxide molecules bind to hemoglobin and block the possibility of oxygen transfer to tissues. A completely new substance is formed – carboxyhemoglobin, which prevents the transport of oxygen, and oxygen deficiency develops very quickly in the body. The concentration of carbon monoxide in the air is directly dependent on the degree of poisoning, and the period of time during which a person inhales poisoned air is also important. The main danger is that carbon monoxide is invisible and not noticeable in any way, it has neither smell nor color, that is, the cause of the ailment is not obvious, and it is not always possible to detect it immediately. Carbon monoxide cannot be felt in any way, which is why its second name is the silent killer. Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning:
- nausea;
- headache;
- rapid breathing;
- dizziness;
- weakness, fatigue;
- chills, drop in body temperature;
- confusion.
It should be noted that debilitated people with chronic diseases, especially those accompanied by anemia, as well as the elderly, pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the effects of CO. Due to acute poisoning, hypoxia can occur very quickly – oxygen deficiency, which leads to irreversible changes in the functioning of the heart and brain. Severe poisoning is characterized by the following symptoms:
- paralysis;
- long-term loss of consciousness, coma;
- convulsions;
- pupil dilation;
- involuntary emptying of the bladder and intestines;
- increased heart rate up to 130 beats per minute;
- cyanosis (blue) of the skin and mucous membranes;
- breathing disorders – it becomes superficial and intermittent.
First aid
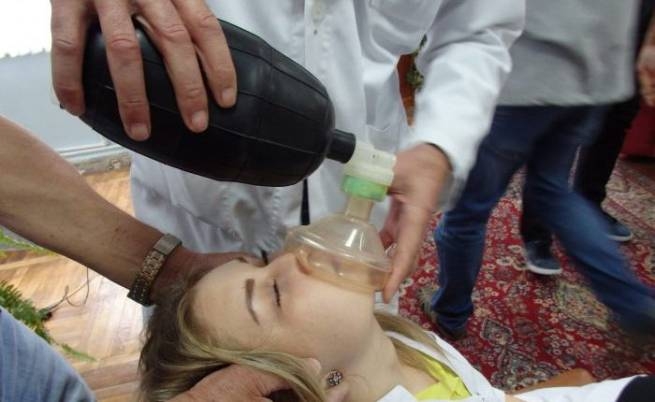
If danger symptoms appear and there is a suspicion that carbon monoxide may be to blame, immediately turn off all appliances and open windows. Call emergency and medical services for help. For the victim, first aid is extremely important. If possible, take him out into the fresh air, unfasten clothing that restricts breathing, give him hot sweet tea and wrap him up warmly when he is chilly. It is necessary to stimulate breathing: bring ammonia, rub the chest, warm the limbs. If the condition is too severe, resuscitation should begin while waiting for an ambulance.






More Stories
"Great" return of Greeks to Athens from Easter holidays
Greece: Private laboratory doctors go on strike on Wednesday
Travel Off Path named 7 popular tourist destinations where tourists are no longer welcome. Greece… among them