Allergy or pseudo-allergy? Scientists have not reached a consensus on the term, but such an atypical reaction of the immune system can cause a lot of trouble.
Most often, allergies to cold occur in geographical latitudes with pronounced seasonality, but this is not at all necessary – ice cream, a cold drink, and even a computer mouse can become an irritant.
What is a cold allergy?
An allergy is an atypical reaction of the human immune system to an external irritant (allergen). How does the body react to cold if, in fact, there is no allergenic substance? Cold allergy is increased sensitivity to low temperatures. It can appear when swimming in cold water, being outside at sub-zero temperatures, and sometimes any cold object or even a drink can become an irritant.
Symptoms and manifestations
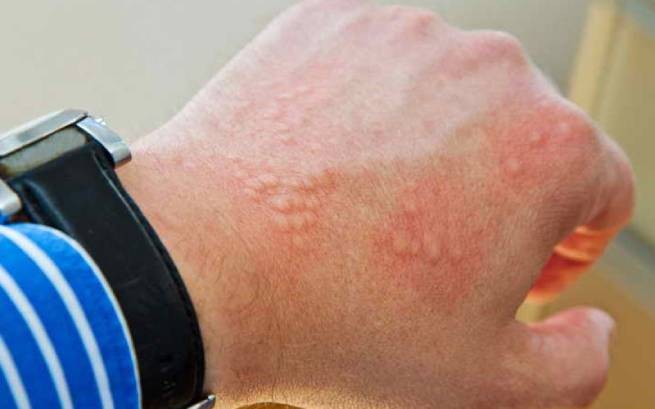
Most often, cold allergies can be confused with allergic dermatitis – the symptoms are similar. For a person suffering from cold allergies, after just a few minutes of being outside in winter, the skin begins to itch and hurt. It turns red, pink or whitish spots of varying sizes and blisters appear on it.
Basically, this type of allergy manifests itself on the face and those parts of the body that are less protected from the effects of cold (for example, on the neck). Cold allergies on the hands and feet are possible, in the form of redness, tingling and itching, since the hands are often not protected by gloves, and only trousers or tights protect the calves, knees and thighs from the cold (unlike warm jackets and coats on the top). body).
On the face, an allergy to cold manifests itself in the form of redness on the cheeks, swollen lips and eyes, cracks in the corners of the mouth and on the lips. Manifestations in the form of conjunctivitis (swelling, redness, inflammation of the eyes, lacrimation) or rhinitis (runny nose, hoarse voice, dry cough) are common.
Sometimes the dermatological reaction spreads to larger areas of the body, and general health worsens: weakness is felt, the temperature rises, the heartbeat quickens, and the head hurts. Symptoms may persist for several hours and usually resolve after returning to warmth.
Causes of cold allergies
This reaction of the body to cold is associated with dysfunction of the immune system. However, scientists have not yet established the exact causes of this pathology. Perhaps, they believe, in the body of some people with hypersensitivity, certain types of proteins are synthesized, under the influence of which histamine, a mediator of allergic reactions, is activated. As a result, the body’s reaction to cold is similar to the reaction when encountering allergenic substances. Sometimes the reason lies in heredity.
What triggers an abnormal reaction to cold?
Among the factors that can cause an inadequate reaction of the body to cold, scientists name:
- predisposition to allergies;
- history of infections (hepatitis C, syphilis, infectious mononucleosis);
- autoimmune diseases, hemophilia, systemic vasculitis, malignant neoplasms;
- taking certain medications (oral contraceptives, tetanus serum);
- bathing in cold water or dousing for the purpose of hardening;
- a sharp change in temperature in winter when leaving a warm room outside;
- being outside in strong winds;
- very cold drinks or ice cream.
Diagnostics
The simplest test will help determine the presence of an allergy to cold at home:
Place an ice cube on your wrist, hold it for four minutes and observe the reaction for 15-20 minutes. If itching, burning, swelling or blistering occurs, the test is considered positive. Sometimes, with high sensitivity to cold, the reaction can occur within 30 seconds, and sometimes it lasts up to 20 minutes.
In case of an acute allergic reaction to low temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor for laboratory diagnosis. The doctor will also question you to clarify your symptoms, heredity, the presence of chronic diseases, and lifestyle. The doctor will order blood and urine tests and skin tests. In some cases, even laboratory diagnosis can be difficult.
How to deal with cold allergies
As in the case of other types of allergies, you need to eliminate the irritant, that is, stay in the cold and wind as little as possible. If itching, redness, tingling, or slight swelling occurs, you should go into a warm room. In case of severe swelling and a sharp deterioration in health, you must immediately contact a medical facility.
Important: with all types of allergies, there is a risk of developing Quincke’s edema (suffocation) or anaphylactic shock (sharp critical drop in blood pressure), so in case of an acute allergic reaction, you should not self-medicate and postpone a visit to a specialist.
If you experience symptoms of the disease, you need to contact an allergist to find out the cause and prescribe treatment. To relieve symptoms, doctors prescribe various medications if necessary. It is important to identify underlying conditions that may contribute to cold urticaria. For example, treatment for hepatitis C may lead to resolution of hives.
To solve problems – the disappearance of symptoms of the disease, a significant reduction in its severity or the achievement of long-term remission – two or three appointments with a specialist are often sufficient.





More Stories
What to do if attacked by a dog (video)
Greece – a paradise for gourmets
Message from AEK and PAOK fans in defense of Esphigmenou Monastery