An outbreak of cases of listeriosis, caused by the Listeria bacterium, has been reported in 7 countries, prompting the ECDC to sound the alarm.
According to health authorities and ECDC scientists, outbreaks have been recorded in countries where citizens consumed fish products. It should be noted that Listeriosis is a serious infection classified as a zoonotic disease caused by eating food contaminated with the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. The ECDC report dated Wednesday (06/19) said there were 73 cases and 14 deaths between 2012 and 2024. Countries where cases occurred:
- Belgium (5),
- Czech Republic (1),
- Germany (39),
- Finland (2),
- Italy (1),
- Netherlands (20),
- UK (5).
The most affected group are men over 60 years of age. Most patients told scientists that they had consumed fish products before they became ill.
Epidemiological information and case tracking have not yielded significant conclusions to “blame” any single factor. However, tests have shown that strain spread geographically in Europe within a few years, and fish products are the most common source of infection. ECDC calls on states to be vigilant and prepared to take corrective measures at industrial sites where biological contamination of products is detected.
According to EODY scientists, listeriosis is a serious infection that causes a severe clinical picture in newborns, adults with a weak immune system and serious complications in the fetus (in pregnant women the disease is mild). However, according to international literature, Pregnant women are 13 times more likely to contract listeriosis than other healthy adults.
The peculiarity of this disease is that, although many people may consume the same contaminated food at the same time, only the most vulnerable become ill, for example, women during pregnancy. As a rule, in pregnant women the disease is mild, but complications of the disease are serious for the fetus. It is therefore recommended that pregnant women, in addition to practicing basic personal hygiene and safe food handling, avoid the following foods as they are considered high-risk foods:
- Smoked, boiled and dried meat.
- Soft cheeses (e.g. katiki, antotiro) and semi-hard cheeses.
- Unpasteurized milk and dairy products derived from it.
- Raw seafood (including sushi) or cold smoked salmon.
- Ready-made raw salads.
- Pre-cooked meat products that can be consumed without further cooking.
- Pate.
- Soft ice cream without packaging.
- It is advisable to avoid eating from fast food restaurants. If a pregnant woman wants to dine out, it is recommended to visit a restaurant where the rules of hygiene, preservation and preparation of food are strictly observed.
Listeria is very stable in the external environment. They persist for a long time in feces, grain, soil, and reproduce successfully at refrigerator temperatures (4-5°C). However, they die very quickly when heated or under the influence of disinfectants with chlorine.
At home, due to the ability of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes to multiply even in refrigerated conditions, it is recommended:
- Preserve foods to be consumed in the refrigerator at ≤ 5°C.
- Timely consumption of food (within 2-3 days from the moment they are placed in the refrigerator).
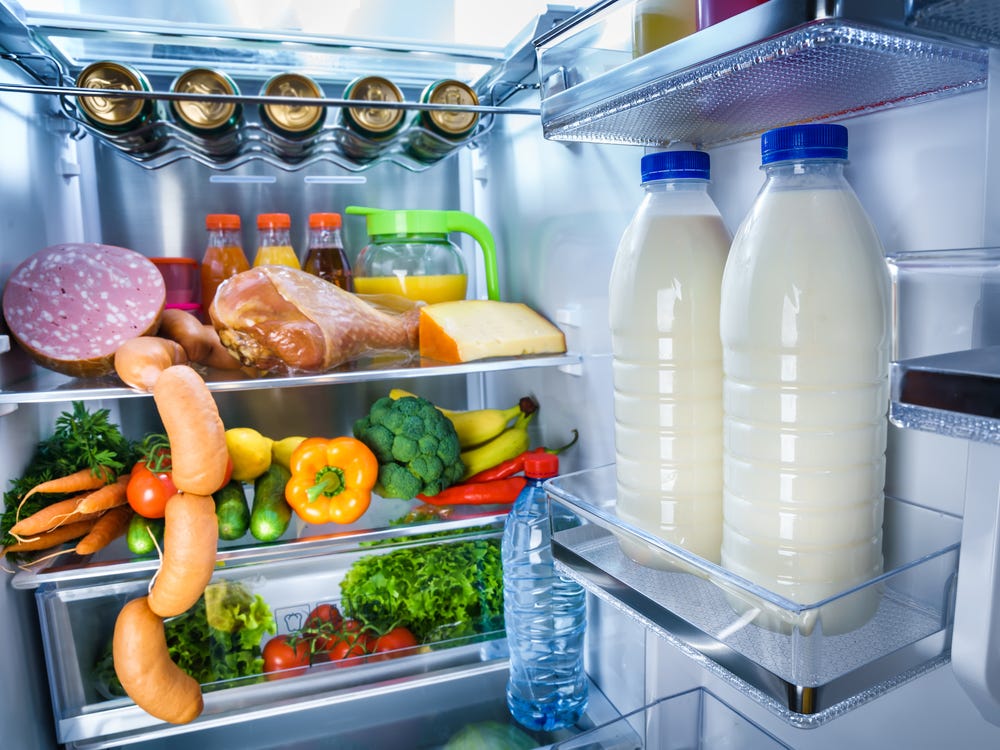

Listeria is ubiquitous. The reservoir of infection in nature is mouse-like rodents. Listeria is also isolated from domestic animals (pigs, rabbits, cows, horses, chickens, ducks). Listeria is found in feed (silage, grain, hay), in human feces, as well as in a wide variety of products. The possibility of Listeria penetration into plants through roots from the soil has been proven. City residents get sick more often, especially in the summer. The main route of infection is through the mouth, most often from eating food contaminated with bacteria. Infection through human contact with a sick animal is less important.
Listeria contamination of foods from the refrigerator is very high – they are found in mayonnaise, smoked fish, meat, salad greens, and on the surface of sprouted grains. Therefore, the main way to combat this is to keep the refrigerator perfectly clean. It is necessary to wash the inside of the refrigerator once a week with chlorinated water. It is also recommended to cook animal products, wash and boil fresh vegetables and herbs for seasoning, and store raw foods separately from boiled or ready-to-eat foods. And after you have cut raw vegetables or meat, the knife and cutting board should be thoroughly washed (and not cut bread on it).





More Stories
Caution: Medicines That Increase the Risk of Sunburn
Diabetes: How much does risk increase for those who sleep in bright light at night?
Red Eyes: Learn about the 15 Most Common Causes