Professor of seismology Gerasimos Chouliaras expressed his competent opinion, speaking about the consequences of an earthquake if such an event happened not in Turkey, but in Greece.
After expressing the views of colleagues (Efthymios Lekkas and Gerasimos Papadopoulos), Professor of Seismology Gerasimos Chouliaras was invited to express his attitude towards two strong earthquakes in Turkey.
“Today is the fourth day after two strong earthquakes in Turkey and Syria. The geological fault is too far from Greece for it to affect us in any way. The distance is too great,” he said, speaking Thursday morning on the SKAI channel.
The professor explained that the term “domino” does not refer to tectonic plates: the epicenter, as he explained, is located more than 1000 km from the territory of Greece: “We saw the domino effect immediately after the earthquake measuring 7.8 on the Richter scale, after the first earthquake, after 9 hours at an altitude of 1000 km there was an earthquake measuring 7.5 on the Richter scale.
When asked Could there have been an earthquake of this magnitude in Greece?, he replied: “Historically, we have had earthquakes of this magnitude, so no one can rule out such a possibility. There have been 3-4 such events of equivalent magnitude in the past, so no one can rule it out.”
When the seismologist was asked what the consequences of such an earthquake would be if it happened in Greece, he said: “It will have less consequences, our buildings are better than those we see in Turkey, we have better infrastructure. Besides there is an advantage in the geodynamics of Greece that the strongest earthquakes occur in underwater areas, so its strength is partially “quenched”“.
Mr. Juliaras concluded: “Buildings are what we need to pay attention to, constant inspections of buildings and infrastructure are the main thing. If we strictly follow the anti-seismic legislation during construction, we will be fine.”
As the “Athenian News” wrote earlier, what happened in southern Turkey on February 6 hasn’t happened in over a century.. An extremely strong earthquake of magnitude 7.9 shook the Earth at 3:17 am. The affected area is located on the border with Syria. After the main earthquake, there were about 42 aftershocks (tremors) with a magnitude of more than 4.5, and at 13:23, there was another shock, even more powerful than the previous one. The exact death toll is rising by the hour.
But what is the root cause of all this? Couldn’t this have been predicted? Why do earthquakes occur? And why in some cases these are small “shocks”, and in others – the destruction of entire cities? The Earth’s crust is divided into many plates that “slide” over the Earth’s mantle, sometimes meeting and causing earthquakes.
Moreover, in addition to collision, these plates can move away from each other (thus opening up a new ocean) or move horizontally relative to each other. All these movements of the plates of the earth’s crust generate ruptures in the rocks: if these ruptures are subjected to displacements, we speak of “faults”. It is faults that generate earthquakes: gaps, therefore, in the earth’s crust. The rupture and displacement of the fault generate seismic waves. When an earthquake occurs, two general types of waves are generated that propagate from the hypocenter (the point deep in the earth’s crust where a rupture occurs, generating/moving a fault). There are two types of waves: P-waves, which only cause compression in the material they pass through without causing damage, and S-waves, which are shear waves and cause real damage during an earthquake. Therefore, the points on Earth where the collision of plates occurs are the most dangerous from a seismogenic point of view. It was at one of these critical points that the earthquake occurred in Turkey.
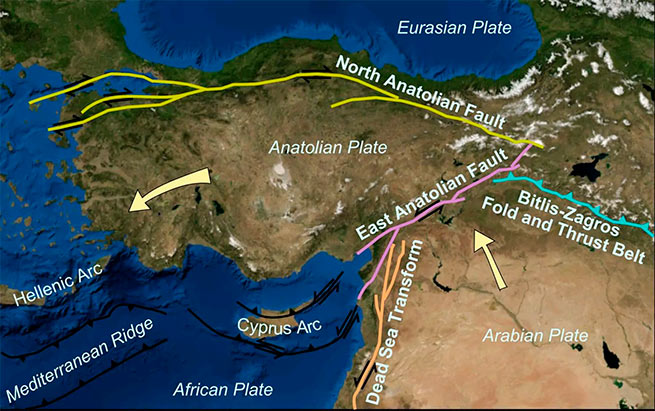
Let’s analyze the “crime scene” to understand what exactly happened at that moment in the earth’s crust. If we pay attention to the picture below, we can see that the earthquake occurred in an area where there are at least 3 mega-faults that demarcate different tectonic plates! The arrows in the figure indicate the movement of each plate. The following faults are affected: East Anatolian and North Anatolian.
They are at the point where the Anatolian Plate, the African Plate and the Arabian Plate meet. Thus, the indicated location is at a very critical triple point in the earth’s crust, where several movements of the earth’s crust take place.
In particular, the epicenter of the earthquake was located in the sector of the eastern part of the East Anatolian Fault, hundreds of kilometers long. This fault is part of a larger structure, namely the North Anatolian fault, which is about 1000 km long. The longer the faults, the higher the earthquake magnitudes can be. The final cause of the catastrophic earthquake in Turkey is due to the sudden movement of the East Anatolian fault, which provoked the collision of the Anatolian and Arabian plates, giving rise to other faults in the process.
Will there be further aftershocks in southern Turkey? Given the existing faults, it is likely that they will, although it is impossible to estimate exactly on what scale. Predicting an earthquake is basically impossible.. However, it is possible to determine which place on Earth is most prone to earthquakes.






More Stories
Orange sky…
African dust: suffocating atmosphere in Attica
Large fire in the area of the Souda naval base on Crete